Grammar – A set of rules to make a language meaningful.
Parts of Speech –
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Adjective
- Verb
- Adverb
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
Phrase – a group of words without a complete meaning
- Noun phrase
- Adjective phrase
- Adverb phrase
Sentence :-
- A group of words with a complete meaning
- Arrangement of words (Structure)
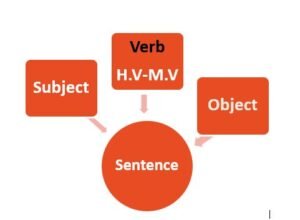
Sentence – 2 parts – Ravi singh loves me.
here – Ravi is a “Subject”
here – loves me is a “Predicate”
Sentence Types – (i) Structure (ii) Function
- Structure –
- Simple sentence – sub + verb + obj.
- ex. Aanchal has done his work.
- Compound sentence – Independent sent. +(counj.)+ Independent sent.
- ex. Kunika has done his work and Mahi liked it .
- Complex sentence – Independent sent.(principal clause) Dependent sent. (subordinate clause)
- Ex. I know Raju, whose books are stolen.
- here – ‘I know raju’ is a – principal clause
- here – ‘whose books are stolen’ is a – subordinate clause
- Ex. I know Raju, whose books are stolen.
- Simple sentence – sub + verb + obj.
- Function-
- Declarative sentence/Assertive sentence.
- Positive sentence – (S +HV+MV+O)
- Ex. Neha singh will know the direction.
- Rohan has done the work.
- Raunak will come.
- Negative sentence – (S+HV+NOT+MV+O)
- Ex. Neha singh will not know the direction
- Positive sentence – (S +HV+MV+O)
- Interrogative sentence (?)
- Close ended(yes/no) – (HV+S+MV+O+?)
- ex. Do you love me?
- Open ended (explain) – (Question word + HV + S + MV + O……?)
- ex. what are you doing?
- Close ended(yes/no) – (HV+S+MV+O+?)
- Imperative sentence – V(1) + OBJ ; do not + V(1) + obj
- ex. Keep quiet
- Help me
- Exclamatory sentence (sudden feelings)
- Wow! I have got a new scooty.
- How pretty you are !
-
Oh no! I missed my train!
-
Wow! You have scored full marks.
-
Alas! He is no more.
-
Hurray! We won the match.
- Optative sentence – wish, curse, bless, pray
- ex. God bless you
- Get well soon my dear.
- Declarative sentence/Assertive sentence.
Modal Auxiliary
:- Helping verbs which represent the mood(attitude) of the speakers.
1.Pure modal auxiliary –
may – might
can – could
will – would
shall – should
have to/has to – had to
ought ot – must
2.Defective/semi modal auxiliary
need, dare, used to
Recent Posts:-
